Financial technology (fintech) has experienced a notable surge in the new normal due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The potential of higher user penetration and a significant rise in digital transactions in the future has set the pace for the advancement of fintech.
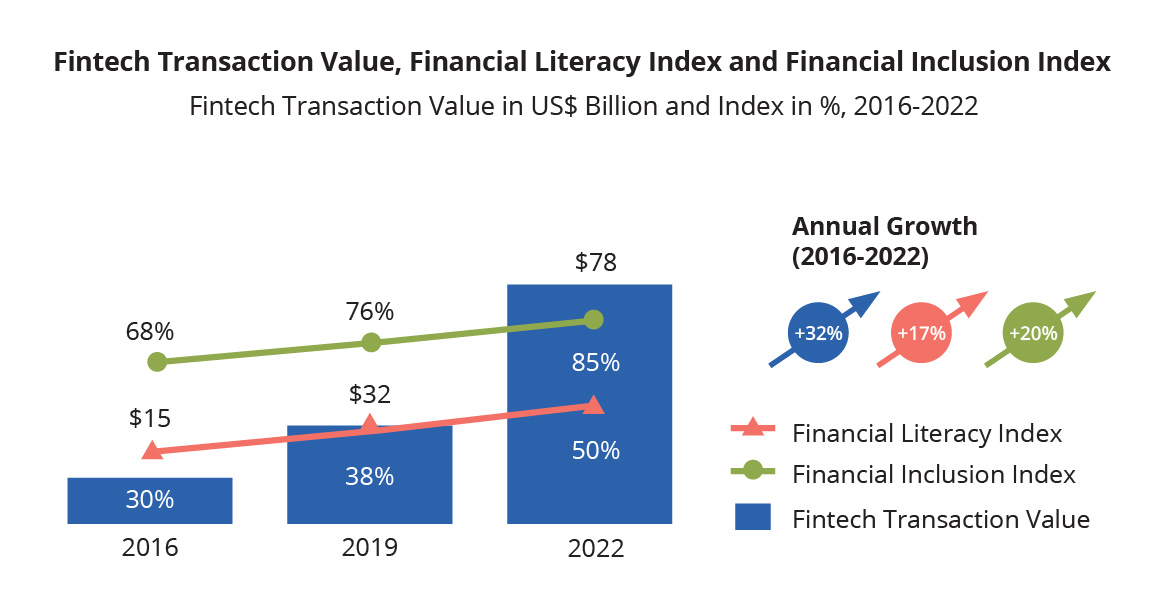
Indonesia’s fintech sector holds a promising future and is anticipated to drive its transaction value, as highlighted in the East Ventures – Digital Competitiveness Index (EV-DCI) 2023. This positive outlook is closely linked to the undeniable connection between fintech transaction volume, financial literacy, and financial inclusion.
Financial literacy involves knowledge, skills, and confidence that shape attitudes and behaviors for better decision-making and financial planning, ultimately enhancing well-being. Financial literacy empowers individuals to make informed choices about products and services that suit their needs. On the other hand, financial inclusion means individuals and businesses have access to useful and affordable financial products and services that meet their needs – transactions, payments, savings, credit, and insurance – delivered responsibly and sustainably.
The EV-DCI 2023 report reveals a remarkable increase in digital transactions, surging by 32% compared to 2019. This surge is accompanied by a 17% rise in financial literacy and a substantial 20% improvement in financial inclusion, indicating progress in awareness and access to financial tools for greater economic stability and prosperity.
Source: Statista – Fintech Indonesia OJK – SNLIK 2022
Drive fintech adoption forward with existing momentum
One of the primary drivers of fintech’s success in Indonesia is the rapid adoption of digital payment platforms. These platforms have simplified transactions such as e-wallet, internet banking, and Quick Response Code Indonesian Standard (QRIS), facilitating the shift from traditional offline to online financial activities. Before the onset of the pandemic, digital wallet usage stood at only around 10%. However, throughout 2020, there was a significant increase in the percentage of digital wallet usage, reaching 44%.
Lockdowns and social distancing during the pandemic expedited the embrace of online shopping, turning e-commerce into a lifeline for consumers and businesses. The result? A remarkable 40% YoY e-commerce growth in e-commerce during the first semester of 2022. Even more impressive is that 53% of e-commerce users favored e-wallets, highlighting the growing trust in digital payments.
Challenges on the fintech advancement roadmap
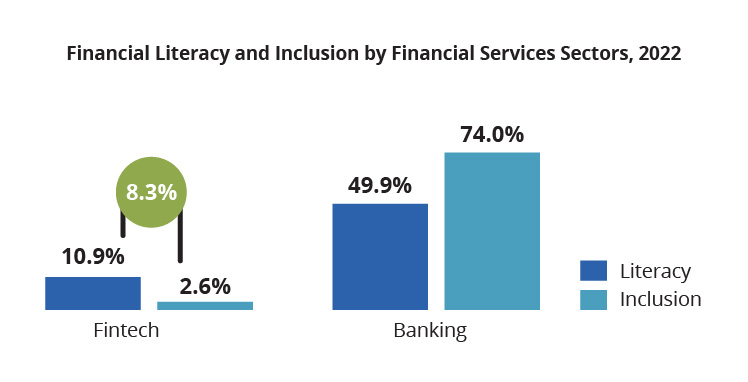
Despite the impressive growth in the fintech sector, specific challenges must be addressed. According to Financial Services Authority (OJK), an 8.3% gap exists between financial literacy and inclusion in the fintech platforms. It signifies that some individuals are aware of fintech services but need more means to access them.
Source: OJK: Survei Nasional Literasi dan Inklusi Keuangan (SNLIK) 2022
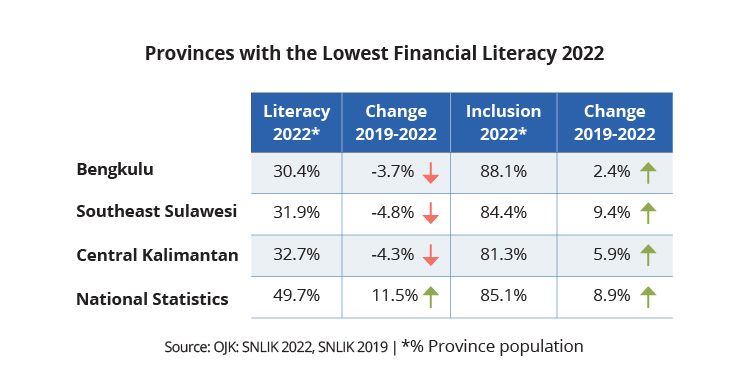
Disparities in financial literacy and financial inclusion are also apparent in some provinces. Bengkulu, Central Kalimantan, and Southeast Sulawesi have high level of financial inclusion but low financial literacy scores. It indicates that residents have access to financial products but need a more comprehensive understanding of these offerings. The knowledge gap exposes them to the risk associated with illegal fintech lending. Between 2018 and 2022, authorities closed 4,432 cases of illegal fintech lending, underscoring the gravity of the issue.
Source: Financial Services Authority, 2022
Strategic approach towards digitalization initiatives
The Indonesian government has taken proactive steps to address these challenges by implementing the National Strategy on Indonesian Financial Literacy (Strategi Nasional Literasi Keuangan Indonesia / SNLKI) for 2021-2025. The strategy aims to achieve 90% financial inclusion by 2024.
Under this strategy, several initiatives have been launched, including creating Massive Open Online Courses (MOOC) and providing a financial calculator on the OJK website for assessing financial health and devising sound financial plans.
Fintech players, including companies and associations, have aligned their initiatives with the SNLKI strategy. A prime example is East Ventures-backed Islamic financial technology platform, Hijra (formerly ALAMI) . Hijra’s innovative business model aims to enhance financial inclusion and literacy. Hijra’s key strategies involve funding MSMEs, benefitting over 1,000 enterprises that previously struggled to access loans from traditional banks, and helping over 4,000 Islamic startups and MSMEs through mentorship, courses, workshops, and funding. The initiatives exemplify how fintech entities bridge financial gaps and foster financial literacy in underserved population segments.
The journey toward equitable financial inclusion through fintech in Indonesia is marked by progress, challenges, and collaborative solutions. With strategic governmental initiatives, innovative fintech players, and an increasing societal embrace of digital finance, it is well on its way to becoming a more financially inclusive and empowered nation.
Download the EV-DCI 2023 report here.